tree in bud opacities pneumonia
Malignancy can be associated with the tree-in-bud sign. Tree-in-bud TIB opacities are a common imaging finding on thoracic CT scan.

Tree In Bud Pattern Pulmonary Tb Eurorad
Studies have reported that pulmonary TB accounts for only 28 of the cause of tree-in-bud opacities as opposed to pulmonary apical granulomas and fibrosis being more suspicious of.
. Cytomegalovirus pneumonia in a 51-year-old man with chronic myelogenous leukemia who underwent bone marrow transplantation. Bacterial pneumonia or tuborculosis. His respiratory condition initially improved but he experienced clinical relapse with a 380C fever and CRP of 1159 mgdL and resumed oxygen therapy.
In radiology the tree-in-bud sign is a finding on a CT scan that indicates some degree of airway obstruction. Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported. TREE-IN-BUD OPACITIES FOR CAD SYSTEMS ULAS BAGCI JIANHUA YAO JESUS CABAN ANTHONY F.
Malignancy can be associated with. 87 rows In the acute phase bacterial pneumonia manifests in the form of segmental or lobar. SUFFREDINI TARA N.
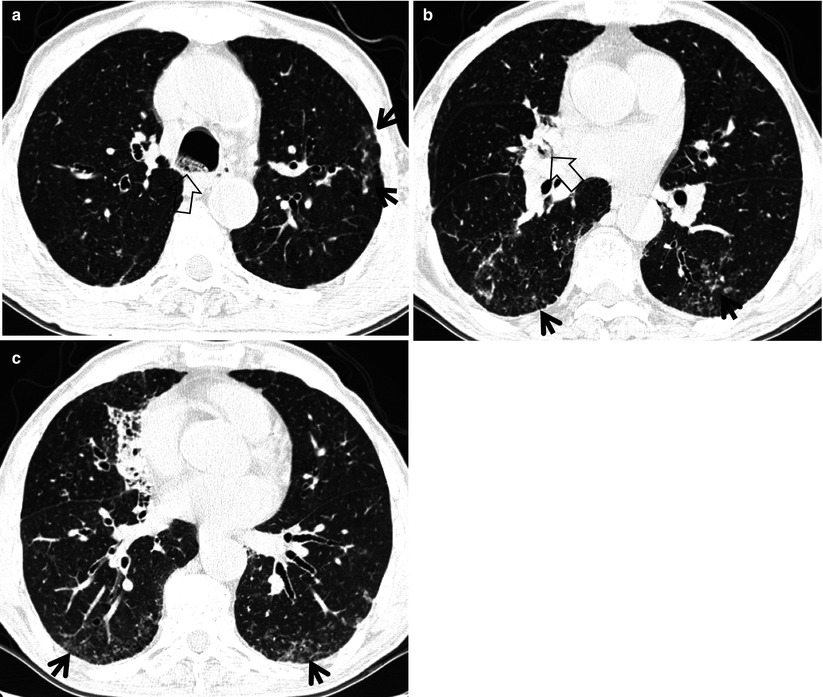
The tree-in-bud pattern can be an early sign of disease Fig 10 15. The differential diagnosis of tree-in-bud nodules includes infection and aspiration the two most common causes as well as congenital airway diseases allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis follicular bronchiolitis panbronchiolitis intravenous injection of foreign material and intravascular tumor emboli. His fever persisted until day 9 when HRCT revealed centrilobular micronodules with treeinbud opacities throughout both lung fields Figure 1B.
CT finding of centrilobular nodules with TIB opacities was first described in pulmonary tuberculosis and is considered highly predictive of. Whereas CT ground-glass opacities are common in COVID-19 but nonspecific vascular tree-in-bud is a unique CT finding that may be. The purpose of this study was to determine the relative frequency of causes of TIB opacities and identify patterns of disease associated with TIB opacities.
Tree-in-bud TIB appearance in computed tomography CT chest is most commonly a manifestation of infection. The differential for this finding includes malignant and inflammatory etiologies either infectious or sterile. However gram staining and cultures were.
He was isolated in a negative. CT tree-in-bud is most commonly reported in peripheral airways disease related to an infectious etiology. The most common causes were respiratory infections 72 including mycobacterial 39 bacterial 27 viral 3 and multiple 4 infections.
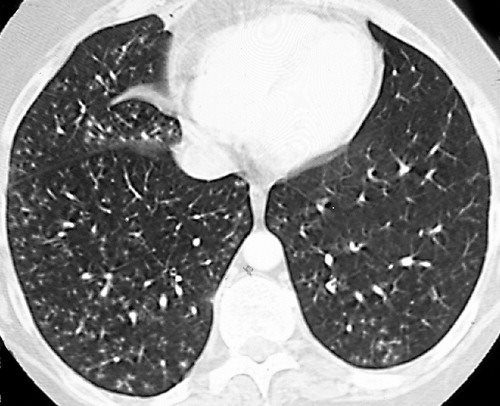
The tree-in-bud sign is a nonspecific imaging finding that implies impaction within bronchioles the smallest airway passages in the lung. A Thin-section CT scan of the right lung shows centrilobular ground-glass opacities in addition to nodules and tree-in-bud opacities arrow. Tree-in-bud TIB opacities are a subset of centrilobular nodules.
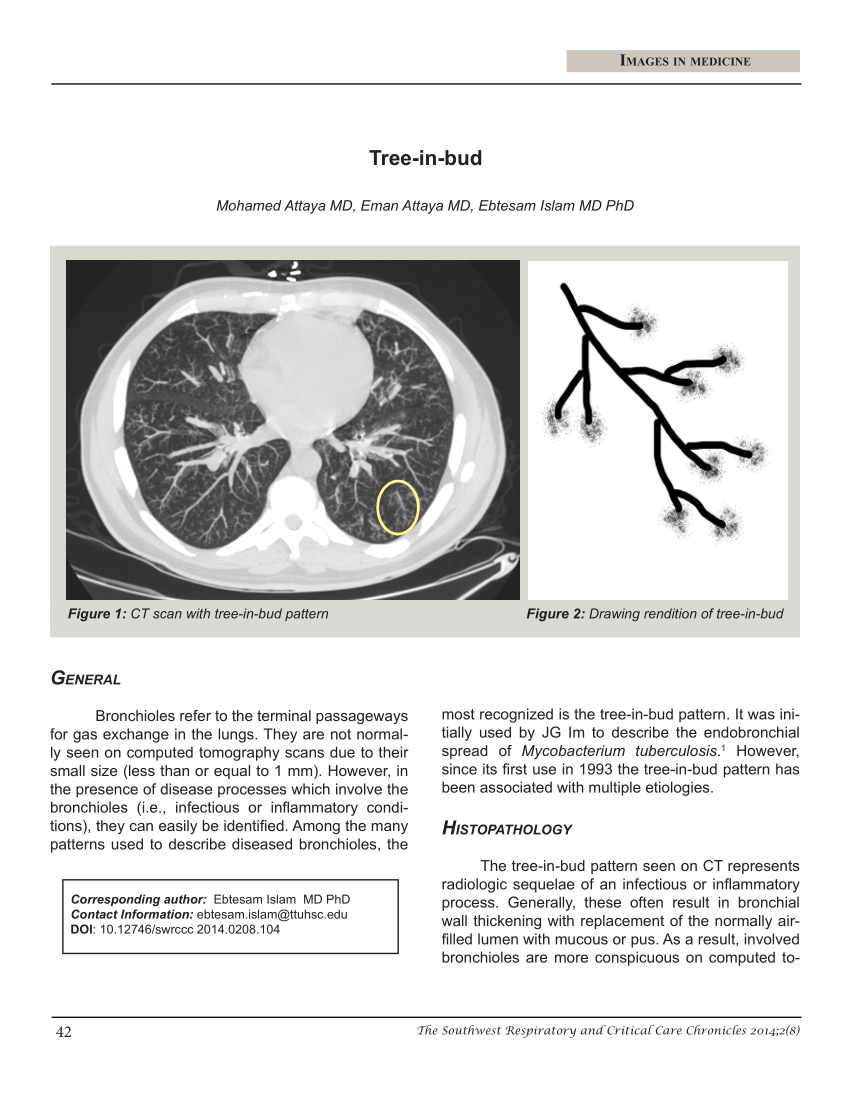
The tree-in-bud pattern suggests active and contagious disease especially when associated with adjacent cavitary disease within the lungs. Bacterial pneumonia or tuborculosis. Tree-in-bud sign refers to the condition in which small centrilobular nodules less than 10 mm in diameter are associated with centrilobular branching nodular structures 1 Fig.
Learning Shape and Texture Characteristics of CT Tree-in-Bud Opacities for CAD Systems. Ad Do you have pneumonia. Ground glass opacity GGO refers to the hazy gray areas that can show up in CT scans or X-rays of the lungs.
The tree-in-bud sign has been described in cases of acute aspiration 13. Find out the 6 common types. TIB opacities typically show branching configurations from secondary pulmonary lobules with sparing of subpleural lungs on CT thorax.
Patients with normal standard physiological pulmonary tests have been shown to have mosaic perfusion and air trapping on HRCT suggestive of bronchiolitis obliterans and a pattern of branching linear opacities like a tree in bud appearance suggestive of bronchiectasis with mucoid secretions. The most common CT findings are centrilobular nodules and branching linear and nodular opacities. 1 refers to a pattern seen on thin-section chest CT in which centrilobular bronchial dilatation and filling by mucus pus or fluid resembles a budding tree Fig.
A young male patient who had a history of fever cough and respiratory distress presented in the emergency department. Learn everything you need to know about pneumonia types. One of such patterns is Tree-in-bud TIB which presents thickened bronchial structures surrounding by clusters of micro-nodules.
The term comes. Though the exact pathophysiological mechanisms for severe COVID-19 pneumonia are not fully known. A Thin-section CT scan of the right lung shows centrilobular ground-glass opacities in addition to nodules and tree-in-bud opacities arrow.
Click to see full answer. These gray areas indicate increased density inside the lungs. Automatic detection of TIB patterns is a challenging.
Tree-in-bud TIB appearance in computed tomography CT chest is most commonly a manifestation of infection. However vascular lesions involving the arterioles and capillaries may simulate. The relative frequency of tree-in-bud opacities in the clinical setting has been evaluated by Miller and Panosian.
One of such patterns is Tree-in-bud TIB which presents textitthickened bronchial structures surrounding by clusters of textitmicro-nodules. However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated. Intravascular pulmonary tumor embolism often occurs in cancers of the breast liver kidney stomach prostate and ovaries and can lead to the tree-in-bud sign in HRCT 214.
We here describe an unusual cause of TIB during the COVID-19 pandemic. Relative Frequency of Tree-in-Bud Patterns in Various Diseases. The small nodules represent lesions involving the small airways.
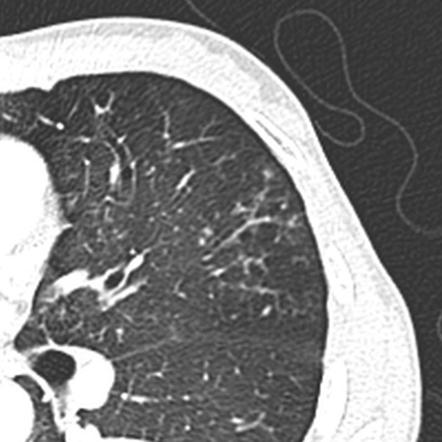
Usually somewhat nodular in appearance the tree-in-bud pattern is generally most pronounced in the lung periphery and associated with abnormalities of the.

Tree In Bud Pattern Semantic Scholar

Pdf Tree In Bud Semantic Scholar
Tree In Bud Sign Radiology Key

Hrct Scan Of The Chest Showing Diffuse Micronodules And Tree In Bud Download Scientific Diagram
View Of Tree In Bud The Southwest Respiratory And Critical Care Chronicles

Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Tree In Bud Sign And Bronchiectasis Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
View Of Tree In Bud The Southwest Respiratory And Critical Care Chronicles

Tree In Bud Pattern Pulmonary Tb Eurorad

Tree In Bud Caused By Haemophilus Influenzae Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
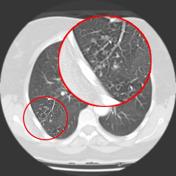
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org